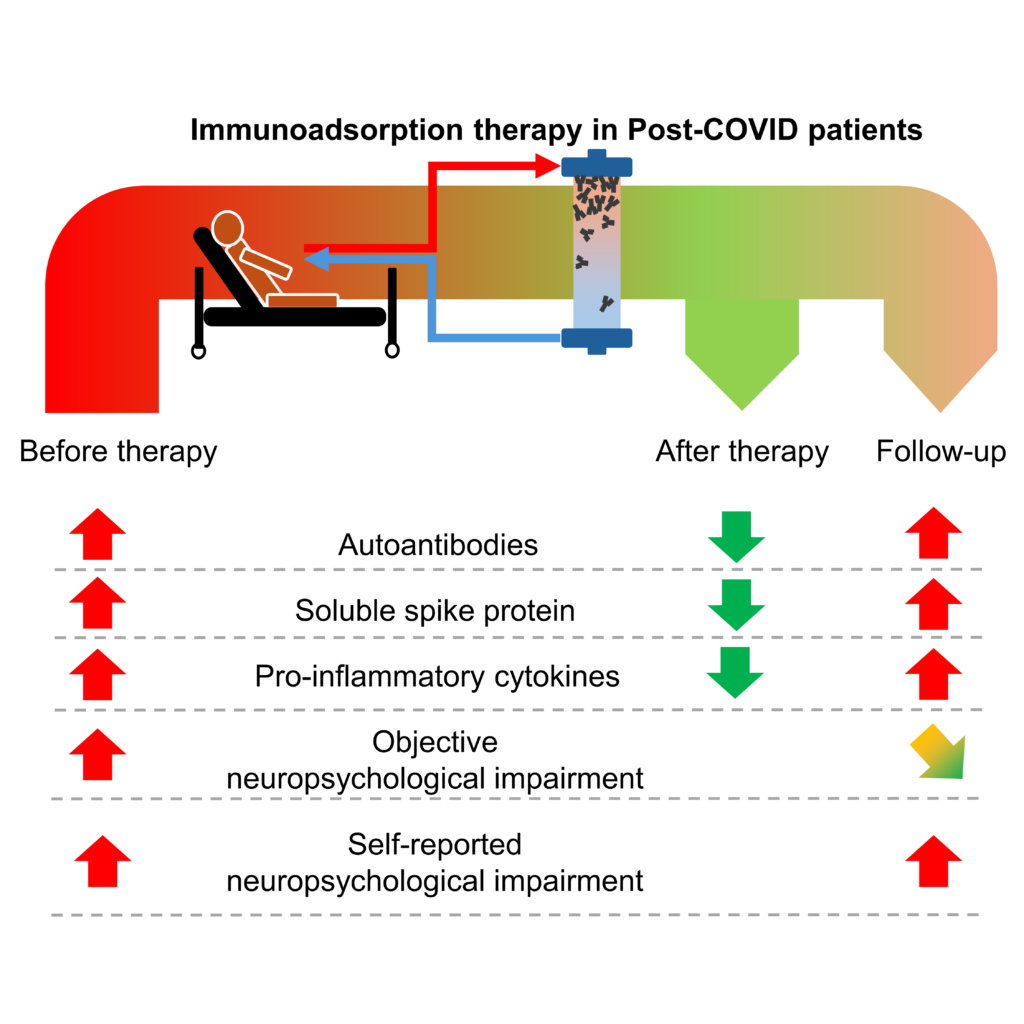
In our latest study, published in the peer-reviewed journal Molecular Therapy, we investigated the effects of immunoadsorption therapy in post-COVID patients suffering from myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS). Twelve patients with elevated autoantibodies targeting the autonomic nervous system and neurological impairments were observed.
Our findings show that immunoadsorption nearly eliminated these autoantibodies while also reducing pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-4, IL-2, IL-1β, TNF, and IL-17A, as well as soluble spike protein levels. Notably, a strong correlation between pro-inflammatory cytokines and specific autoantibodies (β1, β2, M3, M4) was observed in spike protein-positive patients, whereas no such correlation was found in spike protein-negative patients.
Thirty days after therapy, patients exhibited significant improvements in neuropsychological function and a slight but statistically significant increase in hand grip strength. However, self-reported symptoms and ME/CFS questionnaire scores remained unchanged, and the removed proteins showed a rebound within a month.
These findings provide valuable insights into the role of immunoadsorption in post-COVID ME/CFS, but further studies are needed to determine long-term effects and optimal treatment strategies.